Ad Blocker Detected
You must disable your ad-blocking software for our web site in your browser to use this site. You don't have to turn off the ad blocker entirely; just disable ad blocking for codestepbystep.com, then refresh this page to continue.
It is easy to disable a tool like AdBlock for just one site while leaving it enabled for other sites. Just click the "stop sign" icon in the top-right of your browser, then un-check the "Enabled for this site" checkbox. If your UI doesn't match the screenshot below, you may want to Google for how to add a "whitelisted domain" to your ad blocker to allow ads from codestepbystep.com to be shown.
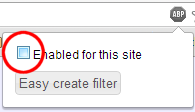
Thank you for your understanding and helping us to keep this service free of cost for all students to use.
Note: If you are seeing this message but aren't running an ad blocker or have disabled your ad blocker:
- Try clearing your browser history and refreshing the page.
- Make sure you don't have any other ad-blocking software running outside of your browser, such as a HOSTS file or proxy.
- If you are using a school computer network: Many high schools have "proxy" software that blocks ads at the entire school level. Your school's system administrator may need to add an exception for codestepbystep.com to allow these ads to get through. You may need to copy/paste this information to your school's network administrator so that he/she can make appropriate changes to your network settings.
If you have questions or need any other assistance, please Contact Us.

 Show/Hide Description
Show/Hide Description